|
Lar
Gibbon
(Hylobates lar) #60-142 |
||||
|
|
Physical
characteristics and distribution
|
|
Hylobates lar weighs 5.5 kg on average. Individuals are either dark brown to black in color, or red buff color with white face-rings, hands, and feet. Colors are not specific to sex. Males and females can show either color, but their white "accents" are always present. H. lar are mainly frugivores, but they will also eat other plant matter. They consume ripe fruit only, and only new leaves and buds. They have several adaptations for feeding. One of them is brachiating locomotion, which involves swinging from branch to branch by their arms. This style of motion allows them to reach the periphery of the tree canopy, where most of their food is found. Other adaptations include high cusps on their back teeth to help grind plant matter, and a gut adapted for a folivorous diet. They rarely, if ever, descend to the forest floor. Lar Gibbons have no fixed season for breeding. The gestation period lasts around seven months, and females produce approximately one young every two years. Young are weaned by the time they are about two years old. In most gibbons, reproductive maturity is reached around 8 years of age. Although they are probably completely capable of caring for themselves at an earlier age, young gibbons do not leave their family group until they reach sexual maturity. Although infants are weaned within a two year period, young stay with the family group for a few additional years. Although the bulk of parental care, including nursing and grooming, is the responsibility of the mother, the father and older siblings also help out. Hylobates lar is found in the tropical rainforests, where it occupies only the upper canopy, between the Slween and Mekong Rivers from S Yunnan (China) south to the Mun River (Thailand) and the Mudah and Thepha Rivers on the Malay Peninsula; S Malay Peninsula south to the Perak and Kelantan Rivers; Sumatra (Indonesia) NW of Lake Toba and the Singkil River; E and E Burma. |
|
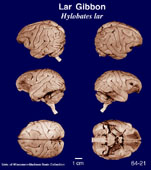
Description
of the brain
|
|
Animal
source and preparation
|
|
All
specimens collected followed the same preparation
and histological procedure.
|
Other Related Resources (websites and publications)
List of Specimens | Explore Collections | Brain Sections | Brain Evolution | Brain Development | Brain Circuitry | Brain Functions | Location and Use | Related Web Sites | Contact Us | Search MSU Database | Personnel | Home