|
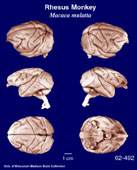
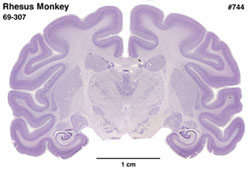
Rhesus
Monkey
(Macaca mulatta) #69-307 |
||||
|
|
Physical
characteristics and distribution
|
|
Rhesus
Monkey Macaca mulatta Head and body length is up to 764 mm and tail length is 25 percent of that. Macaca have been found to breed between the species without any compromise to the offspring's fertility. M. mulatta is likely the most adaptable to a wide variety of habitats and elevations, from high heat to snow fields, to cities. These urban areas offer good shelter and abundance of readily available food. Foraging
occurs mainly on the ground, but M. mulatta is arboreal
and an excellent swimmer. As are all macaques, M. mulatta
is primarily diurnal. Preferred foods include wild and cultivated
fruits, berries, grains, leaves, buds, seeds, flowers, and bark.
Most
social groups range from 8-180 individuals of both sexes, but
there are generally 2-4 times as many females as males. Dominance
hierarchy is more evident among small groups of males than those
with more females who tend to live together more peacefully
than the males. Breeding tends to occur between high ranking
individuals. The job of the males is to defend the group, while
the females form a small internal subgroup to raise the young
macaques whose social status within the troop is inherited from
the mother. M. mulatta is highly vocal sounding a shrill
bark for alarm, barking or screeching as an aggression response,
a scream when under attack, an aggressive growl, and a squawk
of surprise. The
gestation period for M. mulatta is 135-194 days and usually
one baby is born. Infrequently a set of twins is produced. Babies
are nursed for about one year, first clinging to their mother's
bellies and later riding on her back. Sexual maturity in females
is reached between the ages of 2.5 and 4 years, males 2-3 years
after that. Females reach menopause at age 25. M.
mulatta is the sacred monkey of the Hindu religion and is
often found in the vicinity of temples. This species has been
used extensively in the US for research in the areas of biology,
behavior, medicine and even space flight. M. mulatta is found in Afghanistan and India to N Thailand, China, and Hainan Isl (China). |
|
Description
of the brain
|
|
Animal
source and preparation
|
|
All
specimens collected followed the same preparation
and histological procedure.
|
Other Related Resources (websites and publications)
List of Specimens | Explore Collections | Brain Sections | Brain Evolution | Brain Development | Brain Circuitry | Brain Functions | Location and Use | Related Web Sites | Contact Us | Search MSU Database | Personnel | Home